Review of current knowledge and available methods in Mexico, Bavaria and Quebec for sharing water when resources are limited
This project is making use of well-established collaborations with Mexico and Bavaria in order to allow Quebec to initiate the development of a knowledge base on practices and tools for sharing water when it is limited.
Project details
Principal(s) investigator(s)

Context
Water is abundant in Quebec, but its availability can occasionally become a local issue during dry periods. Due to climate change, river flows will be reduced during the summer (longer and more severe depletion) compared to the present. This will increase the pressure on the water supply for populations, wildlife and aquatic ecosystems, as well as for various economic activities (agriculture, industry, tourism, navigation, energy generation, etc.). The water shortages that will arise will require the adaptation of water management practices to ensure sharing between the various uses.
In this context, the development of a knowledge base and the practices and tools developed in other countries would be a useful asset for Quebec in order to identify solutions for sharing and managing water.
As such, Mexico and Bavaria are relevant choices for initiating this work. The links between the research team and academic and government partners in these two locations are already well established and both have faced recent or recurrent water scarcity situations.
Objective(s)
To review the current knowledge and available methods in Mexico, Bavaria and Quebec for sharing water when resources are limited.
Methodology
-
Generate a broad overview of water management by watershed (organizational structure/roles and responsibilities; spatial scales taken into account; amount of surface water and groundwater; type of information exchanged).
-
Expose the context and extent of water scarcity problems.
-
Identify and describe the methods used for water management planning.
-
Identify and describe the preparation, monitoring, and decision-making tools available to communities and other users of water resources.
-
Identify and describe methods for the participation/engagement of civil society and other users of water resources.
-
Indicate how climate change is being addressed and by whom, if applicable.
-
Document the constraints and difficulties encountered as well as the positive elements of the general approach to water management in Mexico and Bavaria, and gather information or testimonies on the perception by the public and water users as well as on acceptability.
-
Organize a workshop with experts in water management in Quebec to present the results, discuss points of comparison with Quebec and identify the most inspiring ideas.
Results
The project generated a comparison of the tools, strategies and current practices in Mexico, Bavaria and Quebec for water management in drought situations.
The figure below is a quantitative summary of the results of this comparison, showing the project’s main elements. The numbering identifying the different aspects of the figure is the numbering used in the methodology.
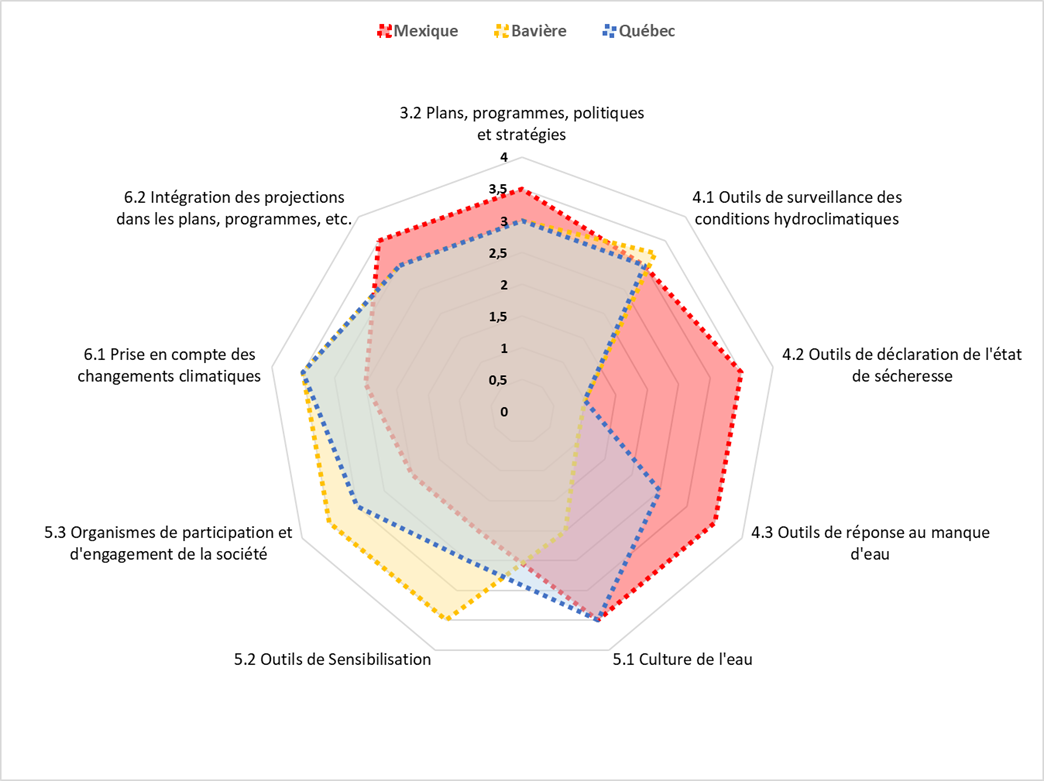
The results obtained identify Quebec’s strengths with regard to monitoring tools for hydroclimatic conditions (4.1), water management plans, programs, policies and strategies (3.2), the existence of a water culture (5.1) and the consideration of climate change (6.1). That said, although the items in points 3.2 and 4.1 are diversified and advanced, they are not yet sufficient for droughts.
The figure also showcases Mexico’s strengths in terms of plans, programs, policies and strategies (3.2), several of which are specifically dedicated to drought situations, as well as drought declaration tools (4.2) and water shortage response tools (4.3). Mexico faces recurring drought situations, particularly in its northern regions.
For its part, Bavaria has advanced hydroclimatic monitoring tools that are beginning to take low water levels in rivers into account (4.1), and provides diverse opportunities for public participation and engagement (5.3) (e.g. river sponsorship), as well as awareness-raising tools (5.2) (e.g. travelling exhibitions loaned by the Bavarian government).
A project like this makes it possible to identify tools, strategies and practices that could improve or complement those used in Quebec, and prepares the ground for conducting a similar information review in other locations (such as other Canadian provinces).
Benefits for adaptation
Benefits for adaptation
Identification of the strengths and areas for improvement in Quebec for water management during droughts that could lead to water shortages
Identification of tools, strategies and practices from other places that could enhance or complement those of Quebec
Scientific publications
Funding
This project is financed by the Quebec government and meets the objectives of the Plan pour une économie verte 2030.

Related projects
709150